

The TF method analogizes the heat conduction problems to dynamic systems, in which heat flux is treated as the input of the system and the temperature profile as the response. The TR method estimates all of the heat flux simultaneously for all time steps and is usually presented as whole time domain form, which often causes heavy computational load. The SFS method is commonly used to solve IHCPs by minimizing the effect of random errors using temperature data at future time steps based on the least square method. Several analytical and numerical methods have been proposed for the solution of IHCPs, such as sequential function specification (SFS) method, Tikhonov regularization (TR) method, transfer function (TF) method, Duhamel’s theory, etc. IHCPs are mathematically ill-posed, and a small error in temperature may significantly affect the accuracy of heat flux estimation. Heat flux is often estimated by surface or internal temperature, which is also termed as inverse heat conduction problem (IHCP). Heat flux is an important parameter to characterize heat transfer performance in many industrial applications, such as thermal protection of space shuttles, thermal management of electronic devices, metal heat treatment, maintenance of boilers and nuclear reactors, spray cooling, geophysics, etc. The effective heat flux of R1234yf can be enhanced by 18.8% by reducing the nozzle diameter and decreasing the back pressure, providing the theoretical basis for the clinical potential substitution of R1234yf with low global warming potential (GWP) for commercial R134a with high GWP in laser dermatology.
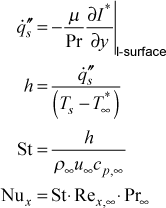
The cooling performances based on 2D filter solution demonstrated that substituting the environment friendly R1234yf for R134a can remarkably reduce global warming potential to <1, but its cooling capacity is insufficient. The maximum heat flux calculated by the 1D method was underestimated by 60% than that calculated by 2D filter solution, indicating that the lateral heat transfer cannot be ignored.
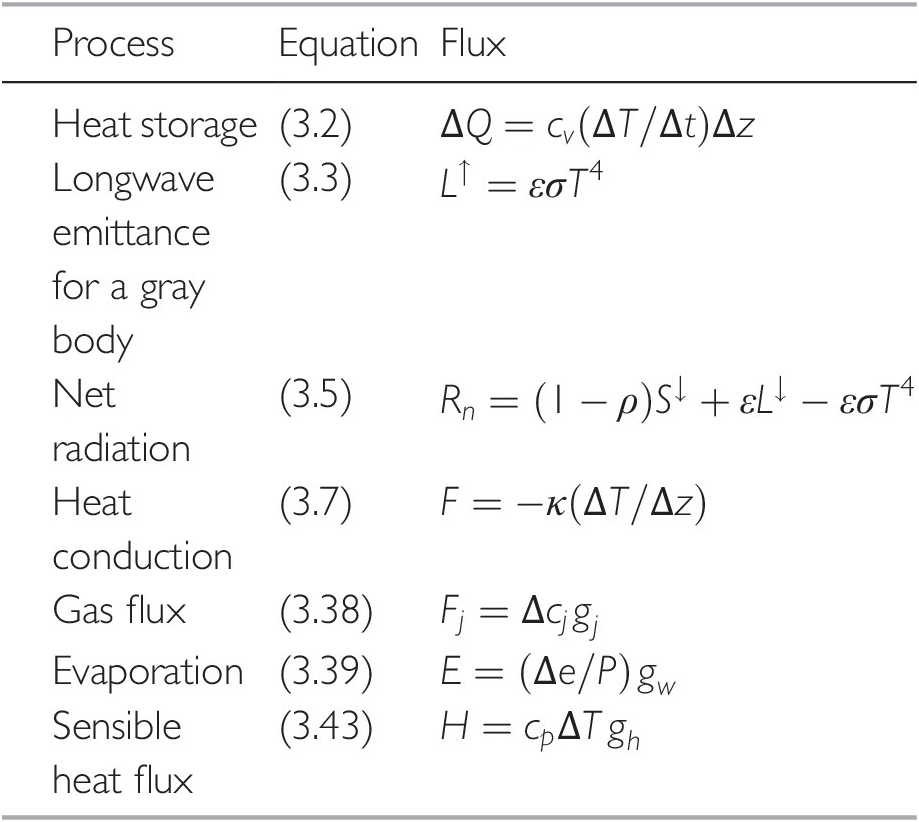
Considering the significant nonuniformity of heat transfer, the 2D filter solution method was proposed to estimate surface heat flux for 2D multi-layer mediums. The Duhamel’s theorem was improved to solve 1D multi-layer ICHP. In this chapter, the available IHCP methods including sequential function specification (SFS), transfer function (TF) and Duhamel’s theorem were compared, taking the example of surface heat flux estimation during spray cooling. Surface heat flux is an important parameter in various industrial applications, which is often estimated based on measured temperature by solving inverse heat conduction problem (IHCP).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
